Firebase is an huge platform to work with, it provides ton of services ready to use (hosting, database, push, authentication, etc). It’s why it make sense to check it for your new projects. On this post I’ll explain how to use the cloud database service.
I’ll start the tutorial from an existing App, if you need some help to create a new Ionic App I recommend to read our post Implementing the Master-Detail Pattern in Ionic. If you’re familiar with Ionic you can follow steps below in any ready Ionic 2 App.

I’ll provide a contact interface, contacts page and ContactsProvider, ./src/providers/contacts/contacts.service, to handle requests to Firebase:
- ./src/pages/
- contacts
- ./src/models/contact.interface.ts
- ./src/providers/contacts/
- contacts.service.ts
Firebase setup
Install required packages
First, let focus on Firebase setup, as first step we’ll install required npm packages to manage firebase connection. Install AngularFire2 (the official library for Firebase and Angular 2) and firebase.
$ npm install angularfire2 firebase --save
$ npm ls angularfire2 firebase --depth 0
/Dvpt/PROJECTS/your-app
├── angularfire2@4.0.0-rc.2
└── firebase@4.3.0
Since npm v3.0.0 peerDependencies no longer cause packages to be implicitly installed. It’s why we need to explicitly installs firebase despite it’s a peerDependency of angularfire2.
Create a firebase project
On Firebase console (need an account, it’s free) create a new project and get config on clicking on “Add Firebase to your web app”.
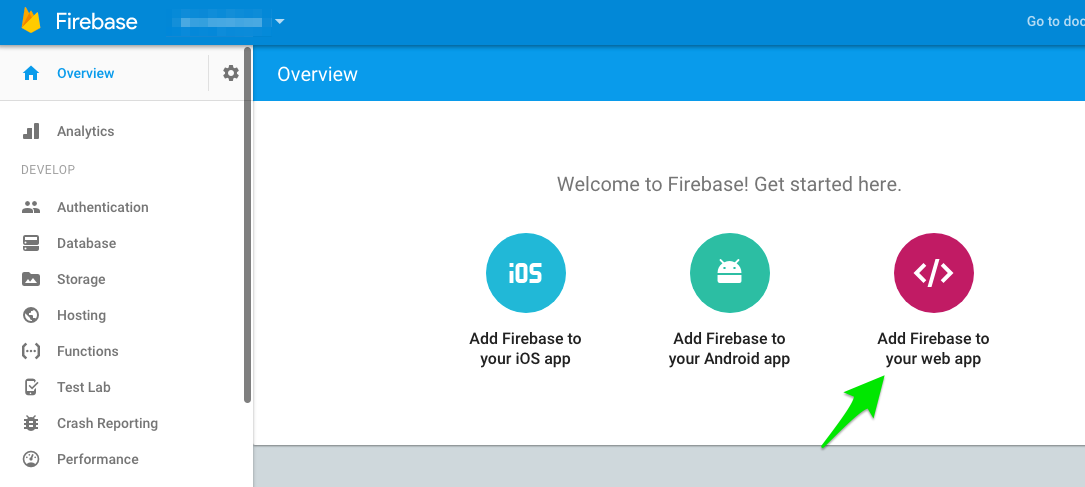
Save the Firebase config
Create ./src/app/app.firebase.config.ts, a new file where you save your firebase config on a constant FIREBASE_CONFIG, looks like:
export const FIREBASE_CONFIG = {
apiKey: "AIzaSyBML2EVs0juvq4wJsjs3gYU-qHJAEu9UiA",
authDomain: "your-app.firebaseapp.com",
databaseURL: "https://your-app.firebaseio.com",
storageBucket: "your-app.appspot.com",
messagingSenderId: "832063717168"
};
Import and setup required modules
Open your src/app/app.module.ts and import required modules:
...
import { AngularFireModule } from 'angularfire2';
import { AngularFireDatabaseModule } from 'angularfire2/database';
import { FIREBASE_CONFIG } from './app.firebase.config';
...
@NgModules({
...
imports: [
AngularFireModule.initializeApp(FIREBASE_CONFIG),
AngularFireDatabaseModule,
...
]
...
})
export class AppModule {}
Right there your app should be able to run without any errors when you do ionic serve.
Data model and first import
Contact interface
Below our Contact interface ./src/models/contact.interface.ts
export interface Contact {
firstName: string,
lastName: string,
title: string,
picture: string
}
First data import
In order to be able to test our code, I provide below an example of data following the contact interface.
{
"contacts":[
{
"firstName":"Luiza",
"lastName":"Bittencourt",
"title":"Supervisora Administrativa e Fiscal",
"picture":"https://s3-us-west-1.amazonaws.com/sfdc-demo/people/caroline_kingsley.jpg"
},
{
"firstName":"Jaime",
"lastName":"Pacheco",
"title":"Departamento pessoal",
"picture":"https://s3-us-west-1.amazonaws.com/sfdc-demo/people/michael_jones.jpg"
},
{
"firstName":"Jonathan",
"lastName":"Bradley",
"title":"Senior Broker",
"picture":"https://s3-us-west-1.amazonaws.com/sfdc-demo/people/jonathan_bradley.jpg"
}
]
}
You can upload this json on firebase database through the console:
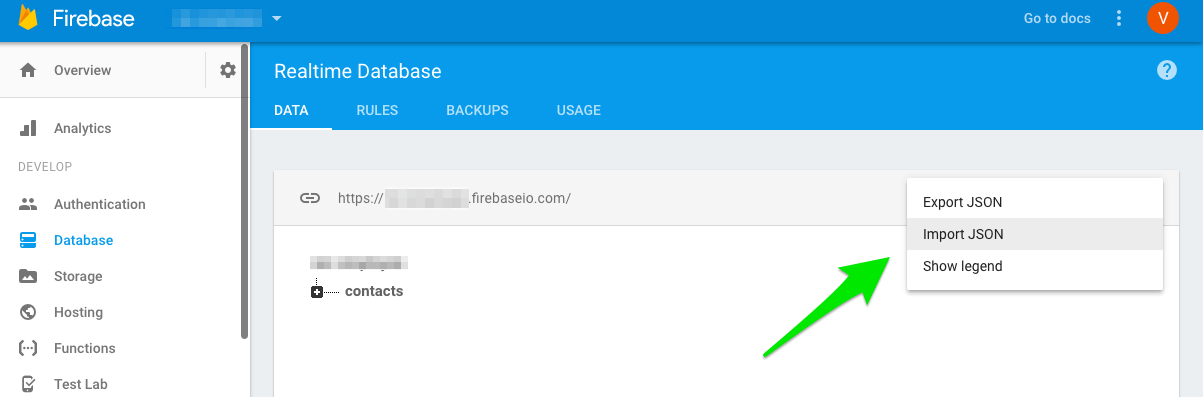
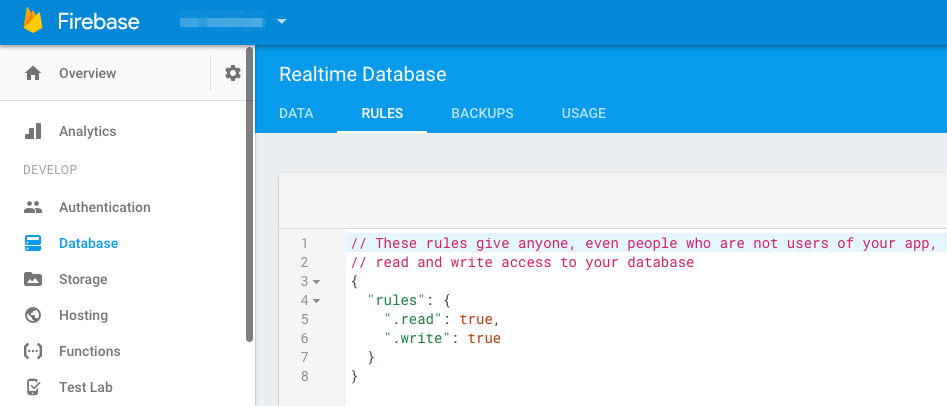
Firebase database rules
By default data has restricted access rules, to allow anyone to read/write you need to update firebase database rules as below:
Contacts Provider to read data from firebase
We use a service provider, ./src/providers/contacts/contacts.service.ts to handle the connection to firebase. Remember to declare your provider on your app module, it’s done automatically if you use ionic generate.
import { Injectable } from '@angular/core';
import { Http } from '@angular/http';
import 'rxjs/add/operator/map';
import {
AngularFireDatabase,
FirebaseListObservable,
FirebaseObjectObservable
} from 'angularfire2/database';
import { Contact } from './../../models/contact.interface';
@Injectable()
export class ContactsProvider {
items$: FirebaseListObservable<Contact[]>;
constructor(af: AngularFireDatabase) {
this.items$ = af.list('/contacts');
}
findAll(): FirebaseListObservable<Contact[]> {
return this.items$;
}
}
ContactsPage
Then,
- our App is configured to load data form firebase
- npm installs
./src/app/app.module.tsand./src/app/firebase.config.ts
- we’ve created an
interface Contactand imported example of data./src/models/contact.interface.ts
- we have a
ContactsProviderto fetch contacts from firebase./src/providers/contacts/contacts.service.ts
So, we are ready to implement our view to display data fetched:
./src/pages/contacts/contacts.ts
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
import { NavController, NavParams } from 'ionic-angular';
import { Contact } from './../../models/contact.interface';
import { ContactsProvider } from './../../providers/contacts/';
@Component({
selector: 'page-contacts',
templateUrl: 'contact.html',
})
export class ContactsPage {
contacts: Contact[];
constructor(
private data: ContactsProvider,
public navCtrl: NavController,
public navParams: NavParams
) {
this.findAll();
}
findAll() {
this.data.findAll().subscribe(
data => {
this.contacts = data;
},
err => {
console.log(err);
}
);
}
}
Contacts View
And now our App is ready to display contacts, edit your Contacts page,
./src/pages/contacts/contacts.html, as below:
<ion-content>
<ion-list>
<button ion-item *ngFor="let contact of contacts">
<ion-avatar item-left>
<img src=""/>
</ion-avatar>
<h2> </h2>
<p></p>
</button>
</ion-list>
</ion-content>
Et voila!!! as exercise you can try to create new contacts within firebase database.